Science and Technology Class 15
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS AND Q&A SESSION (05:06 PM)
SHIPS AND SUBMARINES (05:24 PM)
- Any vessel that is capable of propelling itself beneath the water as well as on the water's surface
- Based on power source there can be two types of submarines
- a) Diesel electric power submarine
- b) Nuclear-powered submarines
- [* SONAR- it can listen to the sound made by the object or it can itself releases high-frequency sound and when it is reflected back, it can listen to the echo]
- Diesel electric power submarine
- Phase I- Initially we brought from Russia- INS Sindhughosh, INS Sindhurashtra, INS Sindhuvijay, etc
- Phase II- As per Project 75 of the Indian Navy an MoU was signed between French company DCNS and Indian company Mazgaon Dock Limited. This deal involved the delivery of six Scorpene-class submarines with elements of indigenization
- Six submarines are- INS Kalvari, INS Karanj, INS Kandheri, INS Vela, INS Vagir, INS Vagsheer.
- These are fast attack submarines that can sustain very high pressure, and have very low acoustics (Low noise), and thus can not be easily detected by SONARs.
- Note- A lot of work is happening to develop Air Independent Propulsion for Diesel Powered submarines i.e. submarines do not have to come to the surface of the water to fulfill oxygen requirements. One way it can be achieved is through electrolysis reaction where electric current is passed through water to recover Hydrogen and Oxygen
- Nuclear-powered submarines
- These submarines are powered by Small Nuclear reactors.
- These submarines can stay inside the ocean for long periods without refueling and they can be propelled at very high speed
- For example- INS Arihant indigenously developed is powered by a pressurized water reactor. It also carries the nuclear-tipped ballistic missile K4. With this capability, India has achieved a "Nuclear Triad" i.e. We can fire Nuclear missiles from Air, Water, and Surface.
-
- Source- Times of India.
TORPEDOES (06:00 PM)
- These are underwater missiles and follow a straight path similar to a cruise missile. For example Varunashtra
-

- India's Torpedo defense system is called Maareech. It is an advanced torpedo defense system for Torpedo detection and countermeasures
-

SHIPS (06:05 PM)
- There are 4 types of ships
- Destroyers- These are large warships equipped with Missiles, Torpedoes, Radars, and Sonars. For example- INS Kolkata, INS Vishakhapatnam, INS Mormugao
-
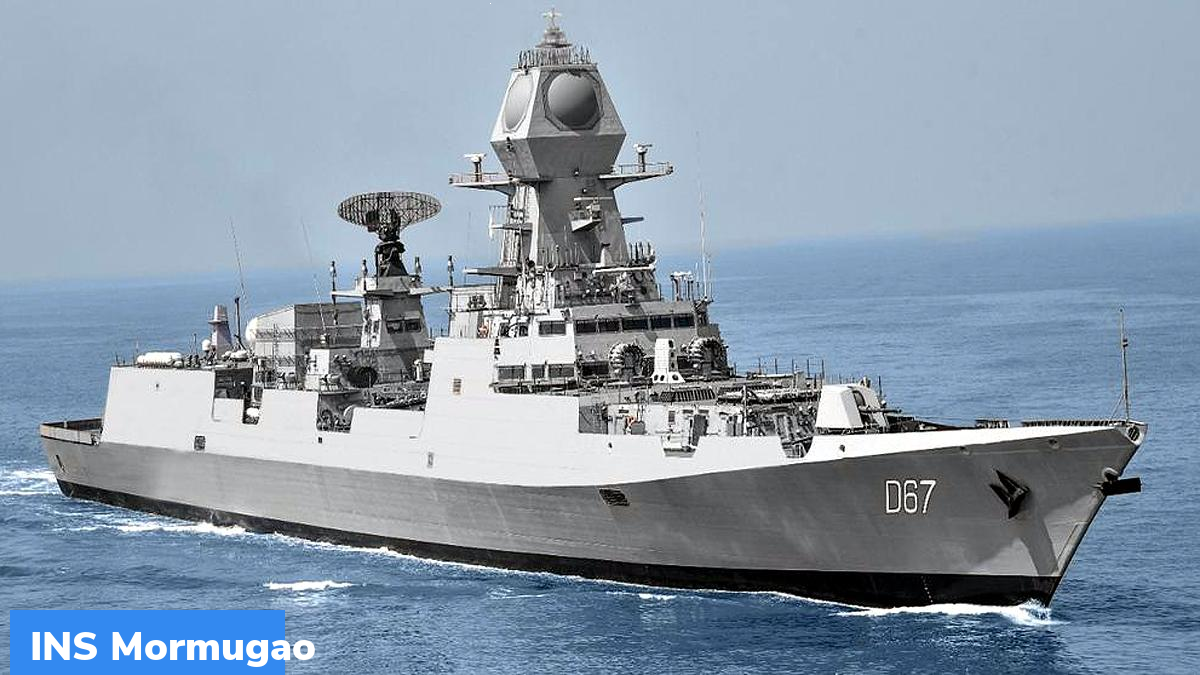

- Frigates are smaller but faster than destroyers. They have both offensive and defensive capabilities. They are used as escort vessels to protect lines of communication. It can also be an integral component of a strike group. It can also be used in Minor warfare. Example- INS Shiwalik, INS Talwar, INS Brahmaputra.
-
- Corvettes- These are often the smallest ship in the naval fleet. They can have applications in coastal patrolling, Minor wars etc. Example- INS Kamorta, INS Kavaratti etc.
- Aircraft carrier (06:26 PM)
- They are floating air bases in the sea, and fighter aircraft operate from their decks. They are often accompanied by destroyers, Frigates, Submarines etc. For example- INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- INS Vikrant-
-

- It is named after the first aircraft carrier of India which played a vital role in the 1971 war. INS Vikrant is 262 meters long uses the STOBAR mechanism has 3/4th of indigenous content and can attain a speed of 28 knots.
- For landing and takeoff, an Aircraft carrier can use STOBAR or CATOBAR system.
- Short take-off but arrested recovery (STOBAR)- The frontal part of the deck is elevated which supports aircraft carriers in taking off as a Ski-jump mechanism. Example- INS Vikrant and Vikramaditya
-

- Catapult Assisted System but arrested recovery (CATOBAR)- Catapult mechanism is kept under the deck which is attached to the wheels of the aircraft. The stored energy of the catapult is released and converted into the kinetic energy of the aircraft. Catapult can be powered by a steam engine or electromagnetic aircraft launch system (EMALS)
-

- In arrested recovery, high-strength arrester wires are placed on the deck. The aircraft has a tail hook that gets arrested in one of the wires and decelerates rapidly.
STEALTH TECHNOLOGY (06:53 PM)
- Radars send out electromagnetic symbols as short pulses which may be reflected by objects in their path in part reflecting back to the radar depending on the time taken, Doppler shift, the speed & direction of an object can be calculated by a radar system.
- Sonar works on the same principle but uses sound waves.
- The purpose of stealth technology is to make an aircraft, ship, or submarine invisible to radar or sonar.
- Following methods can be deployed
- a) Aircraft can be shaped in a way that radar signals are reflected away from the radar equipment.
- b) Aircraft can be covered in materials that absorb Radar signals
- c) Use of Radio jammers- In Radio jamming for a particular frequency noise is maximized so that the receiver will not be able to intercept meaningful signals.
AIRCRAFT (07:10 PM)
- Generation Aircrafts
-

- Source- Times of India
- Parameters on which we divide the generation aircraft- Weapon, Speed, Maneuverability, Stealth features, Air to Air refueling capability.
- Combat Aircrafts
- From Russia- MiG 21, MiG 29, Sukhoi Su 30.
- From France- Mirage and Rafael- Both are developed by Dassault.
- From the UK- Jaguar
- Indigenous- Light Combat Aircraft- Tejas (LCA Tejas)- It is one of the lightest, smallest supersonic fighter aircraft belonging to the 4th generation. It carries Air to the surface, Air to Air precision-guided weapons. It has air-to-air refueling capability. It can carry a maximum payload of 4000 kg and a speed of Mach 2
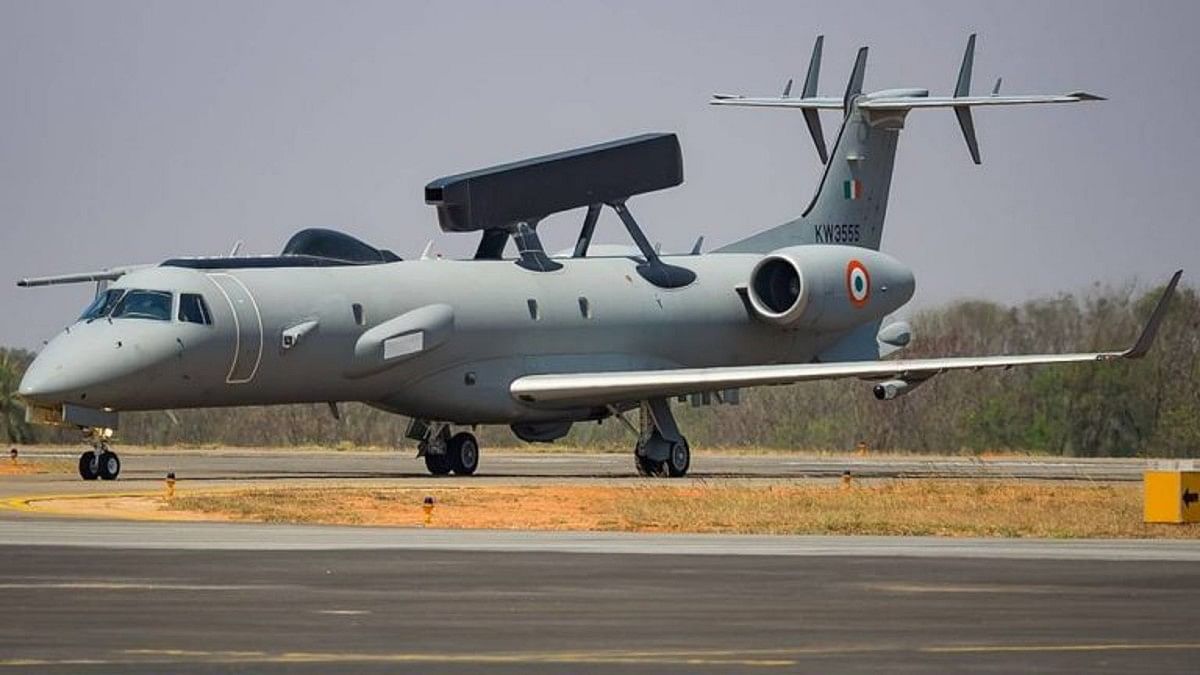
- Airborne early warning and control system (AEW&C)
- It is an Airborne radar system to detect aircraft, ships, missiles, and other incoming projectiles at long range. For example- the Indian airforce has 5 airborne warning aircraft, 3 of Israeli origins named Falcon and 2 indigenous ones named Netra.
-

EMERGING TRENDS IN MODERN WARFARE (07:30 PM)
- Directed energy weapons
- A weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy without a solid projectile that can include a laser beam, electron beam, sound beam, or Microwave among others.
- For example- DRDO is working on a system called KALI (Kilo Ampere Linear Injector) for targeting long-range missiles. It is supposed to emit powerful pulses of electrons that can damage electronic systems on board.
- Weaponization of space
- It means destroying a satellite from the ground (Anti-satellite capability) and putting a weapon system into space that can be used to destroy another space asset or a target on Earth. Currently, USA and China are in a race toward weaponization of space.
- Outer space treaty 1967 is not equipped to deal with recent developments. There is a demand in many countries including India that this treaty needs to be re-negotiated to handle recent developments.
- Hypersonic vehicles
-
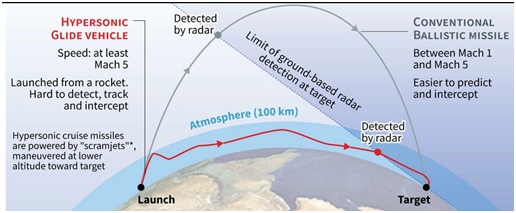
- Hypersonic weapons provide the capability that Radar systems will not be able to intercept and thus such weapons can not be Neutralized easily.
- However, attaining hypersonic speeds in the atmosphere has many challenges
- a) More the speed, the more will be the atmospheric drag
- b) More atmospheric friction leads to very high temperatures in the range of 1000s of degrees Celsius. Very few materials can maintain integrity at such high temperature
- c) They will require air-breathing engines to fulfill their oxygen requirements.
- Air Breathing engines
-

- There are three approaches to design air breathing engines
- a) Jet engine- In the jet engine rotating parts are used to compress the incoming air so that combustion can occur. It can start from zero and can attain speed up to Mach 3
- b) Ramjet- In Ramjet, the forward motion of the vehicle is used to compress air rather than any rotating parts thus Ramjet does not start from zero, it has to use some other mechanism to attain supersonic speed after which Ramjet can become operational.
- c) Scramjet- In a Ramjet engine there are obstructions to airflow because of that combustion occurs at subsonic speed and thus Ramjet can attain hypersonic speed up to Mach 7. In scramjet, the design is changed in a way that no obstruction occurs. Combustion can occur at supersonic speeds and gradually scramjet can attain even higher hypersonic (More than Mach 10).
The Topic for the next class:- Intellectual Property Rights.
